|
NEW PAINLESS MINIMAL INVASIVE SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR THE TREATMENT OF HAEMORRHOIDS
H.A.L: Doppler Guided Haemorrhoidal Artery Ligation Procedure
Director of Department of Surgery, Dr.
A new surgical method for the treatment of haemorrhoids is used in our department with great results.
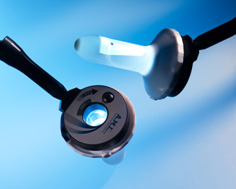
H.A.L - Haemorrhoidal Artery Ligation – is a new form of treatment for grades 2 to 3 of haemorrhoids by ligation of haemorrhoid arteries using a Doppler ultrasound device. This minimal invasive technique effectively targets symptoms without any pain.
By means of the Doppler sensor and audible signals transmitted by the device, the surgeon is able to pinpoint the exact location of the arteries supplying blood to the haemorrhoids. The surgeon then ties off each artery (called ligation) by placing a stitch around it and knotting the ends. Because the stitch is placed not in the anus but in the lower rectum, where there are almost no pain nerves, the whole procedure is virtually painless. All other procedures (scalpel, ultrasonic ligation, laser, coagulation) cause some point postoperative pain.
Besides the absence of pain postoperatively, H.A.L method has the follow advantages:
• Minimal hospital stay (One day’s hospital stay)
• Very high success rates (over 95%)
• No complications
• Minimal recurrence rate
• No need of general anaesthesia
• Short procedure time of around just 30 minutes
• No cutting, no removal of tissue and no open wounds
• Able to return to work the next day
In case of haemorrhoids of 4th grade, (prolapse and protrude from the anus), R.A.R – Recto Anal Repair, technique is used additionally, to suture and lift them back into place
The Doppler equipment for the H.A.L/ R.A.R® procedure, is certified with European ISO and CE-Mark, and is approved by the FDA (Food & Drugs Administration).
REFERENCES
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21228673
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20689288
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18622559
|









